Carbonxide – Powder Additives:
Carbonxide A1
More than 85% Alumina.
Carbonxide A2
Less than 85 of Bauxite small amount of Magnesia.
Carbonxide M1
More than 97% MgO.
Industry sectors
Steel&Iron industry
Aluminium /Non Ferrous Metals
Incineration
Cement
Petrochem
Ceramic
Glass
Sugar …
Technical advantages
Porosity & uniformity of pores
- Predominantly micro pores
- Smooth pore distribution pattern
Thermal diffusivity and capacity
In tranheat sfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It measures the rate of transfer of heat of a material from the hot end to the cold end.
(Unit m²/s.)
(Unit m²/s.)
- is thermal conductivity (W/(m·K))
- is specific heat capacity (J/(kg·K))
- is density (kg/m³)
Strength improved
- Modulus of rupture (MOR)
- Young‘s Modulus (Elasticity)
- Hot Modules of rupture (HMOR) (at 1400°C up to 1600°C)
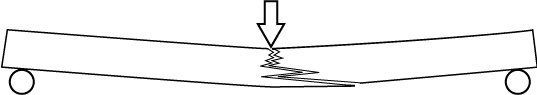
Thermal shock resistance – improved
- Based on uniformity of micro pores
Applications
Dense Refractory Bricks
- Magnesia Carbon Bricks
- High Alumina Bricks
- Refractory Bricks (All Kind)
Prefabricated Parts
Castables (All Kind)
Insulating Firebricks (IFB)
Insulating castables
Process advantages & savings
Thermal insulation – improved
- based on uniformity and small diameter of micro pores
- lower thermal diffusivity
- better insulation – energy saving – less cost for CO2-Emission
Reduced costs
- Longer life times – higher productivity
- Energy saving based on thermal capacity
- Increased use of „Recycling“ materials
- Less use of Binder/Resin
- Less maintenance and production downtimes
Process security/safety
- More residual lining thickness
- Less maintenance – worker protection (dust, etc.)
Refractory Production
- More use of „recycling“ material (Magnesia…)
- Reduced need of raw materials – (Magnesia, Alumina, Resin, etc)
- Less emission from transportation (i.e. trucks etc.)
- Less use of Binder/Resin
In-Situ (During Use)
- Longer Life Time Of Refractory Linings
- Less Repair And Process Changes (I.E. Ladle Transitions)
- Less Need Of Refractory Products – Less Waste
- Better Insulation And Thermal Capacity – Based On Micro Pores
- Energy Saving
- Less CO2-Emission
- Less Maintenance And Production Downtimes
- Support Of Sustainability Of The Process
Environmental & Benefits
Important test procedures
- Hot modulus of rupture – HMOR (Mpa) at 1400°C
- Modulus of rupture – MOR (Mpa)
- Young‘s modulus of elasticity
- Thermal shock resistance
- Thermal diffusivity
- Thermal capacity
- Thermal conductivity (insulation)
- Erosion resistance
- Abrasion resistance
Carbonxide – Powder Additives:
-Carbonxide A1 = more than 85% Alumina
-Carbonxide A2 = less than 85 of Bauxite small amount of Magnesia Spinel
Carbonxide M1 = more than 97% MgO

Industry sectors
• Steel&Iron industry
• Aluminium /Non Ferrous Metals
• Incineration
• Cement
• Petrochem
• Ceramic
• Glass
• Sugar …
Technical advantages
Porosity & uniformity of pores (!)
- Predominantly micro pores
- Smooth pore distribution pattern
Thermal diffusivity
In tranheat sfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It measures the rate of transfer of heat of a material from the hot end to the cold end.
 Unit m²/s.
Unit m²/s.
• is thermal conductivity (W/(m·K))
• is specific heat capacity (J/(kg·K))
• is density (kg/m³)
Thermal capacity (!)
Strength improved
- Modulus of rupture (MOR)
- Young‘s Modulus (Elasticity)
- Hot Modules of rupture (HMOR) (at 1400°C up to 1600°C)
Thermal shock resistance – improved
- based on uniformity of micro pores


Applications
– Dense Refractory Bricks
- Magnesia Carbon Bricks
- High Alumina Bricks
- Refractory Bricks (all kind)
– Prefabricated Parts
– Castables (all kind)
– Insulating Firebricks (IFB)
– Insulating castables
Process advantages & savings
• Thermal insulation – improved
- based on uniformity and small diameter of micro pores
- lower thermal diffusivity
- better insulation – energy saving – less cost for CO2-Emission
• Reduced costs
- Longer life times – higher productivity
- Energy saving based on thermal capacity
- Increased use of „Recycling“ materials
- Less use of Binder/Resin
- Less maintenance and production downtimes
• Process security/safety
- More residual lining thickness
- Less maintenance – worker protection (dust, etc.)


Environmental-Benefits
•Refractory production
- More use of „recycling“ material (Magnesia…)
- Reduced need of raw materials – (Magnesia, Alumina, Resin, etc)
- Less emission from transportation (i.e. trucks etc.)
- Less use of Binder/Resin
•In-Situ (during use)
- Longer life time of Refractory linings
- less repair and process changes (i.e. ladle transitions)
- less need of Refractory products – less waste
- Better insulation and thermal capacity – based on micro pores
- Energy saving
- less CO2-Emission
- Less maintenance and production downtimes
- Support of sustainability of the process
Important test procedures
- Hot modulus of rupture – HMOR (Mpa) at 1400°C
- Modulus of rupture – MOR (Mpa)
- Young‘s modulus of elasticity
- Thermal shock resistance
- Thermal diffusivity
- Thermal capacity
- Thermal conductivity (insulation)
- Erosion resistance
- Abrasion resistance

